
Plant Cell Parts and Structure
What are cells? What makes up a plant cell? Activity - Plant cell structure The differences between animal and plant cells Video Test your knowledge Animal and plant cells quiz Key.
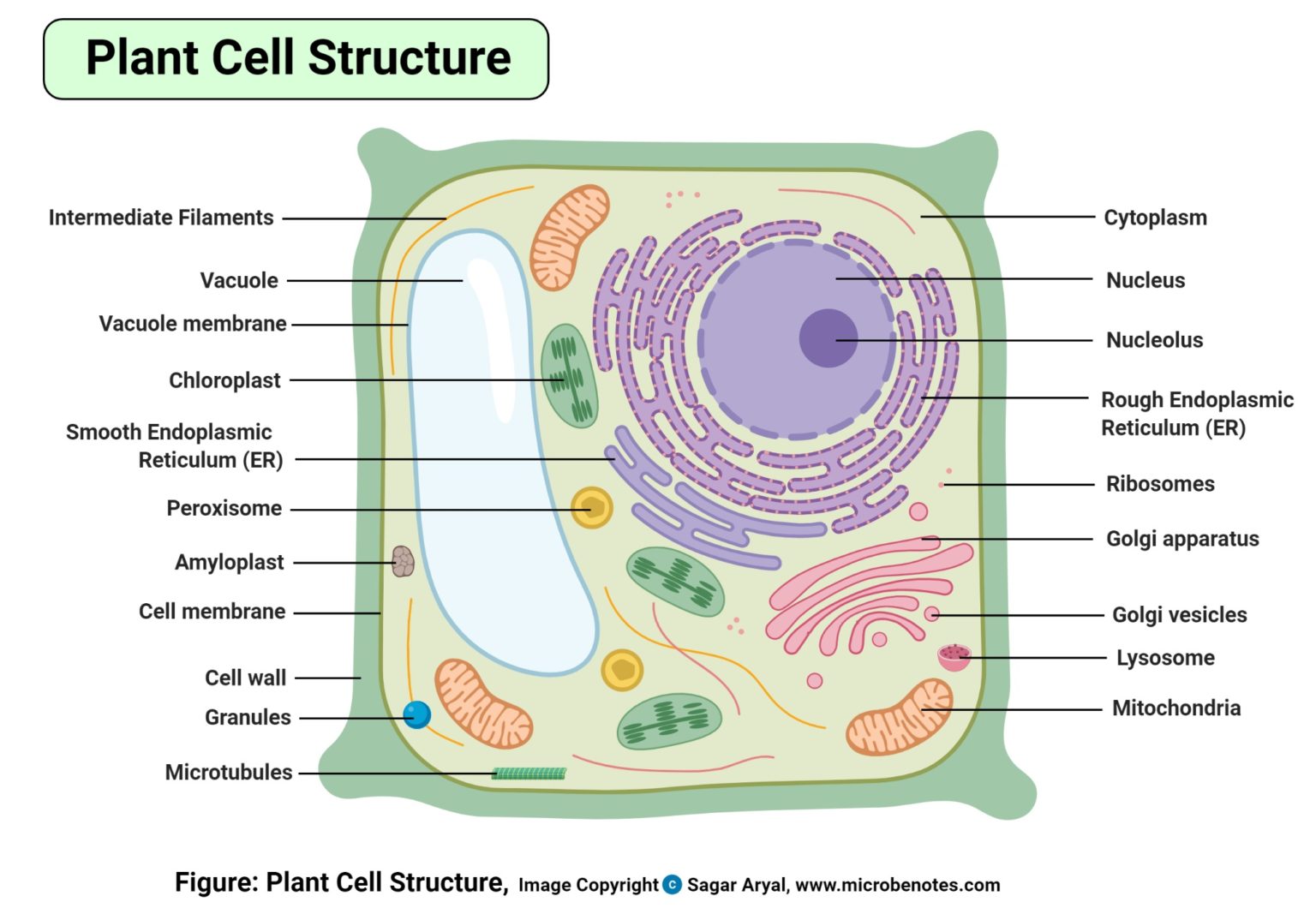
Plant Cell Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram
A diagram of a plant cell with the organelles labeled The plant cell has many different features that allow it to carry out its functions. Each of these structures, called organelles, carry out a specialized role. Animal and plant cells share many common organelles, which you can find out more about by visiting the " Animal Cell " article.

Plant Cell Parts and Structure
Figure 10.1.5 10.1. 5: A micrograph of a cell nucleus. The nucleolus (A) is a condensed region within the nucleus (B) where ribosomes are synthesized. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope (C). Just oustide the nucleus, the rough endoplasmic reticulum (D) is composed of many layers of folded membrane.
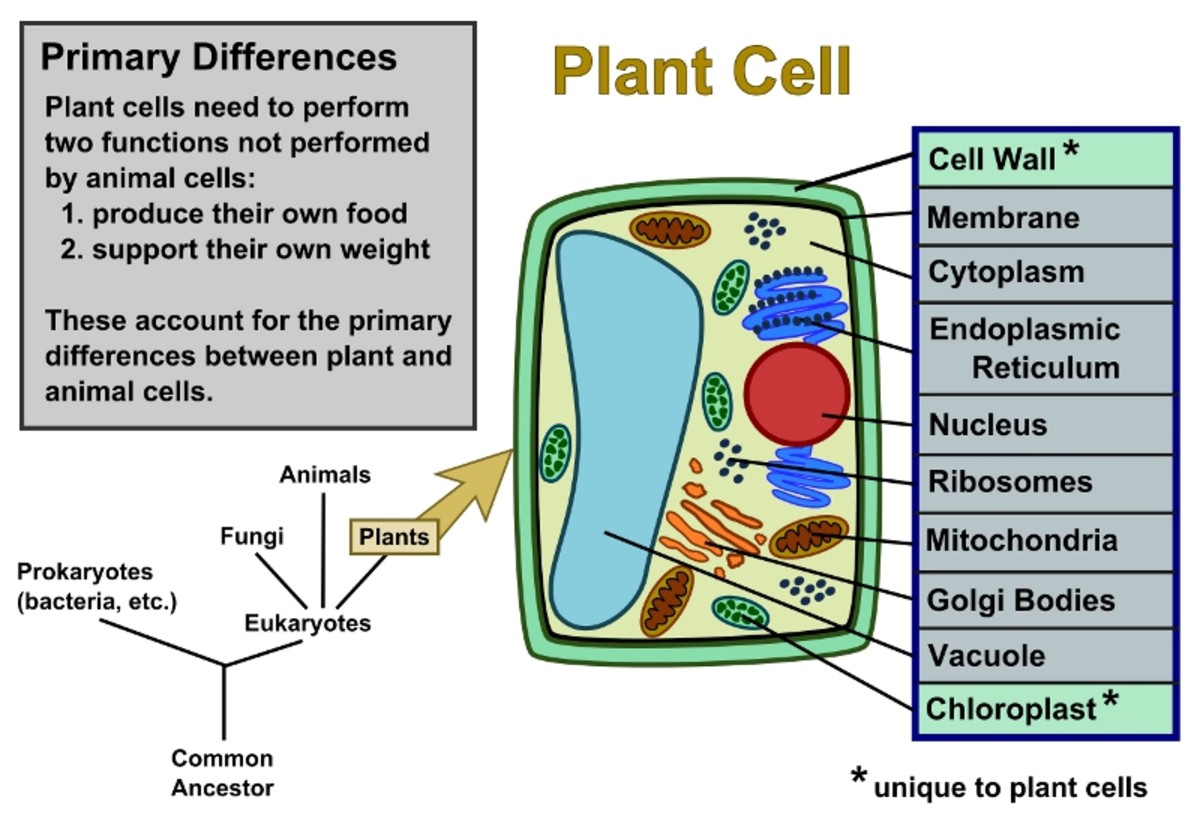
Plant Cells Vs. Animal Cells (With Diagrams) Owlcation
plant cell, the basic unit of all plants. Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. For a more in-depth discussion of cells, see cell. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a cell wall surrounding.
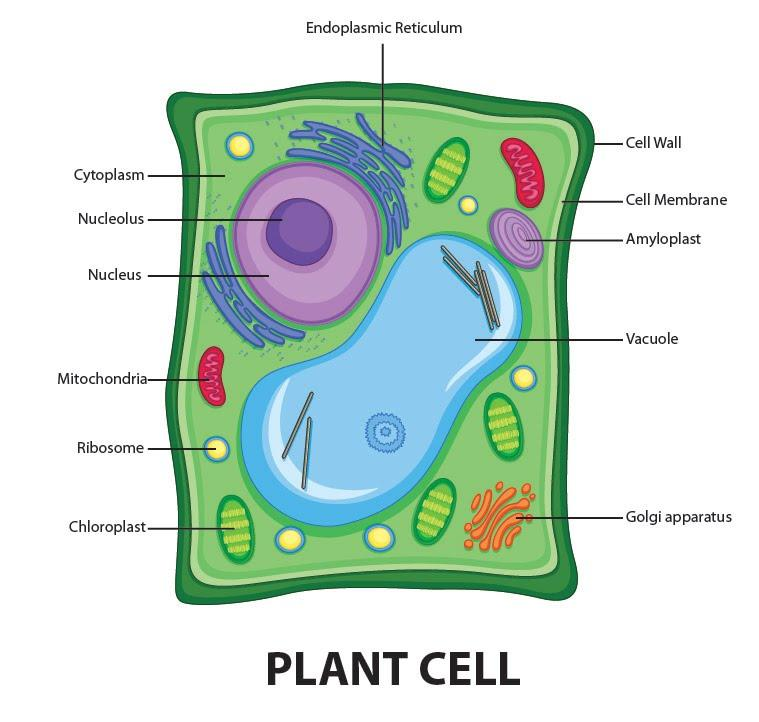
Draw a welllabelled diagram of a plant cell.
Plant Cell Diagram 1) Cell Wall. It is the outermost, protective layer of a plant cell having a thickness of 20-80 nm. Cell walls are made up of carbohydrates such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin and a complex organic polymer called lignin. Functions. Providing mechanical strength, support, and rigidity to the cell; Providing shape to.

Plant Cell Diagram, Definition, Structure, Function & Parts
Diagram of a typical plant cell: Image modified from OpenStax Biology. Both animal and plant cells have mitochondria, but only plant cells have chloroplasts. Plants don't get their sugar from eating food, so they need to make sugar from sunlight. This process (photosynthesis) takes place in the chloroplast.

Plant Cell Parts and Structure
A plant cell is the basic building block of a plant. Plant cells, like all eukaryotic cells, contain a nucleus and other organelles, each with its distinct functions. However, plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from animal, fungal, and bacterial cells. Plant Cell Characteristics Plant cells are eukaryotic.

Pin on GCSE Science paper 1
Plant cells have certain distinguishing features, including chloroplasts, cell walls, and intracellular vacuoles. Photosynthesis takes place in chloroplasts; cell walls allow plants to have strong.

plantcelldiagram Tim's Printables
A plant cell diagram. Plant cell structure Like all organisms, plants have cells. Plant cells have a nucleus with chromosomes and DNA, and they have mitochondria. Those are common to all eukaryotic cells. But in some ways they are different from animal cells and the cells of other eukaryotes .
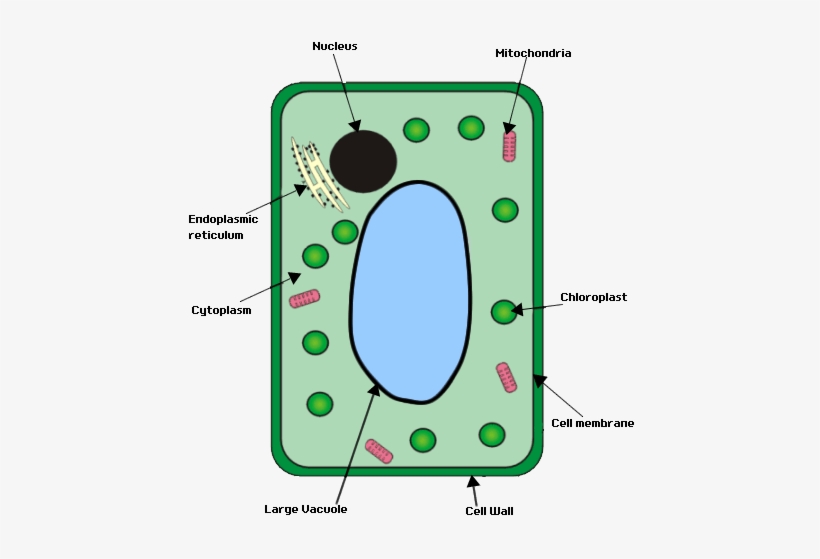
Simple Plant Cell Drawing Free download on ClipArtMag
3. DNA, the heredity information of cells, which can be found in a nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the a nucleoid region of prokaryotic cell. 4. ribosomes, or protein-synthesizing structures composed of ribosomes and proteins. These structures can be found on the image of the plant cell (Figure 3.1.2.1 3.1.2. 1 ).
.svg/1280px-Simple_diagram_of_plant_cell_(en).svg.png)
FileSimple diagram of plant cell (en).svg Simple English Wikipedia
Plant cells This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below - the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal and.

Plant cell diagram Plant cell diagram, Cell diagram, Plant cell
Prokaryotes are organisms which are made up of small and simple cells. Eukaryotes are organisms which are made up of large and complex cells. Animals and plants are eukaryotes. Bacteria are prokaryotes.

Plant Cell Diagram, Definition, Structure, Function & Parts
Key points: All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell, and controls what goes in and comes out. The cell membrane surrounds a cell's cytoplasm, which is a jelly-like substance containing the cell's parts. Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell.

Diagrammatic representation of a generalized plant cell depicting the
Plant Cell: Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram September 16, 2023 by Faith Mokobi Edited By: Sagar Aryal Plant cells are eukaryotic cells, that are found in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae which means they have a membrane-bound nucleus.

Plant Cell Diagram Woo! Jr. Kids Activities Children's Publishing
Plant Cell Definition. A plant cell refers to any cell of a plant. It is the structural and functional unit of plants. Plant cells are presumed to have evolved from the early green algae and probably first occurred in the early Paleozoic era, more than 500 million years ago. Plant cells were first observed by an English natural philosopher.

Diagram Showing Anatomy Of Plant Cell Stock Illustration Download
Structure of a plant cell. Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae.Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capability to perform photosynthesis and store starch, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or.